

“Cosmic-ray particles sneaking into the atmosphere at the Earth’s magnetic poles can create truly astonishing, colourful auroral lights,” said Michael Hajek, External Dosimetry Specialist at the IAEA. Sievert is the measure of health risk from radiation: one sievert carries with it a 5.5 per cent chance of eventually developing radiation-induced cancer later in life. About half of this comes from artificial sources such as X-ray, mammography and CT scans, while the other half we get from natural sources, of which about 10 per cent comes from cosmic radiation. On average, people are exposed to around 3.5 millisieverts of radiation per year. Sometimes, cosmic radiation does reach us, but without creating any harm, just like other low levels of radiation we are regularly exposed to.

The magnetosphere deflects cosmic rays and protects us from solar flares. The Earth is shielded by a magnetic field that makes the charged particles bounce from pole to pole, creating two gigantic donut-shaped belts populated by energetic electrons and protons. Although rare, strong solar flares can eventually create radio blackouts and impact modern communication and navigation technology on ground. Like a rubber band, the Sun’s fields can snap, suddenly releasing enormous energy and presenting potential health concerns to astronauts in space. The remainder comes from solar particle events – sudden and sporadic outbursts of electrically charged particles accompanied by electromagnetic emissions that occur when magnetic fields on the Sun’s surface stretch and twist. Some of this radiation is continuously emitted from the Sun’s corona, which led scientists to call it the ‘solar wind’. Solar cosmic radiation is composed of charged particles emitted by the Sun, predominantly electrons, protons and helium nuclei. The Earth is constantly exposed to galactic cosmic radiation. In essence, supernovas act like huge, natural particle accelerators. The energy released in these explosions accelerates charged particles outside our solar system, making them highly penetrating and extremely hard to shield. Galactic cosmic radiation comes from the remnants of supernovas, which are powerful explosions during the last stages of massive stars that either collapse to black holes or are destroyed. They travel at nearly the speed of light, which is approximately 300 000 kilometres per second.Ĭosmic rays are of two kinds: galactic and solar.
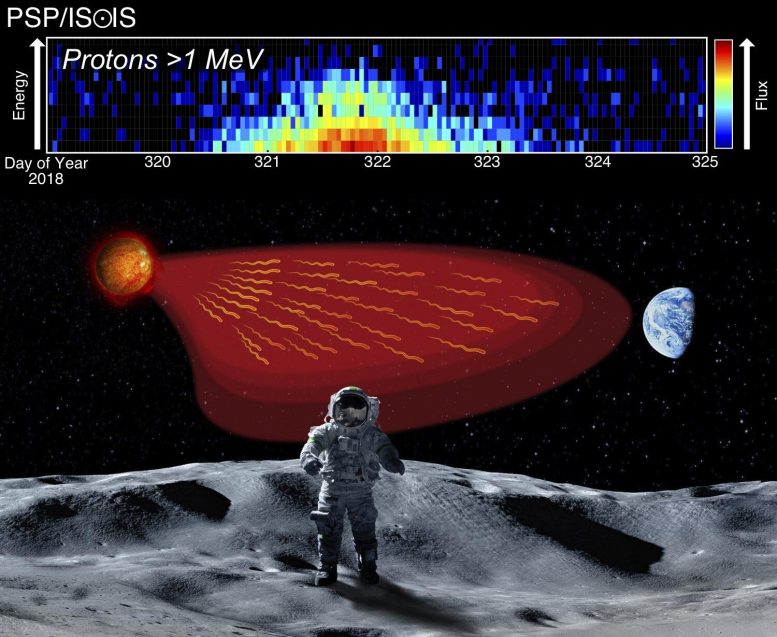

In this article, we explore what it is, why we are protected from it on Earth, how it affects people in specific jobs, and how it can even help advance technology for cancer treatment.Ĭosmic rays are extremely high-energy subatomic particles – mostly protons and atomic nuclei accompanied by electromagnetic emissions – that move through space, eventually bombarding the Earth’s surface. Cosmic radiation is what it sounds like: radiation from space.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
